Page 106 - Pharma News Letter - Vol2 Issue 1
P. 106
Chapter V
Multi-Targeted Anti-Alzheimer’s Agents: Synthesis, Biological
Evaluation, And Molecular Modeling Study Of Some
Pyrazolopyridine Hybrids
European Journal Of Medicinal Chemistry. 2023 Dec; 262: 115880.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Omnia M Waly , Selwan M El-Sayed , Mariam A Ghaly, Hussein I El-Subbagh
Abstract
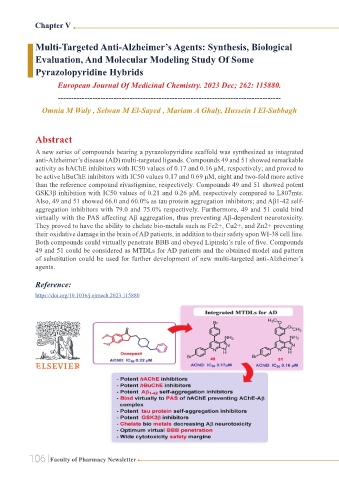
A new series of compounds bearing a pyrazolopyridine scaffold was synthesized as integrated
anti-Alzheimer’s disease (AD) multi-targeted ligands. Compounds 49 and 51 showed remarkable
activity as hAChE inhibitors with IC50 values of 0.17 and 0.16 μM, respectively; and proved to
be active hBuChE inhibitors with IC50 values 0.17 and 0.69 μM, eight and two-fold more active
than the reference compound rivastigmine, respectively. Compounds 49 and 51 showed potent
GSK3β inhibition with IC50 values of 0.21 and 0.26 μM, respectively compared to L807mts.
Also, 49 and 51 showed 66.0 and 60.0% as tau protein aggregation inhibitors; and Aβ1-42 self-
aggregation inhibitors with 79.0 and 75.0% respectively. Furthermore, 49 and 51 could bind
virtually with the PAS affecting Aβ aggregation, thus preventing Aβ-dependent neurotoxicity.
They proved to have the ability to chelate bio-metals such as Fe2+, Cu2+, and Zn2+ preventing
their oxidative damage in the brain of AD patients, in addition to their safety upon WI-38 cell line.
Both compounds could virtually penetrate BBB and obeyed Lipinski’s rule of five. Compounds
49 and 51 could be considered as MTDLs for AD patients and the obtained model and pattern
of substitution could be used for further development of new multi-targeted anti-Alzheimer’s
agents.
Reference:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115880
106 Faculty of Pharmacy Newsletter